Millisievert is from the word Sievert. The American Heritage Dictionary defines it as:
sie·vert (s

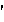 v
v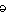 rt) n.
rt) n. A unit of ionizing radiation absorbed dose equivalent in the International System of Units, obtained as a product of the absorbed dose measure in grays and a dimensionless factor, stipulated by the International Commission on Radiological Protection, and indicating the biological effectiveness of the radiation.
The sievert (symbol: Sv). It attempts to quantitatively evaluate the biological effects of ionizing radiation as opposed to the physical aspects, which are characterised by the absorbed dose, measured in gray. It is named after Rolf Sievert, a Swedish medical physicist renowned for work on radiation dosage measurement and research into the biological effects of radiation.
The unit gray measures absorbed radiation which is absorbed into any material. The unit sievert specifically measures absorbed radiation which is absorbed by a person. The equivalent dose to a person is found by multiplying the absorbed dose, in gray, by a weighting factor (W). The weighting factor (sometimes referred to as a quality factor) is determined by a combination of: the radiation type, the tissue absorbing the radiation, and other pertinent factors.
This is SI base units standard:
- 1 Sv = 1 Gy • W (where Sv=sievert, Gy=gray, W=weighting factor specific to each type of radiation and tissue).
therefore:
| Radiation type and energy range | Factor |
|---|---|
| electrons, positrons, muons, or photons (gamma, X-ray) | 1 |
| neutrons <10 keV | 5 |
| neutrons 10–100 keV | 10 |
| neutrons 100 keV – 2 MeV | 20 |
| neutrons 2 MeV – 20 MeV | 10 |
| neutrons >20 MeV | 5 |
| protons other than recoil protons and energy >2 MeV | 2 |
| alpha particles, fission fragments, nonrelativistic heavy nuclei | 20 |
| Tissue type | Factor |
| bone surface, skin | 0.01 |
| bladder, breast, liver, esophagus, thyroid, other | 0.05 |
| bone marrow, colon, lung, stomach | 0.12 |
| gonads | 0.20 |
Because the body has multiple tissue types a weighted sum or integral is often used.










No comments:
Post a Comment